Thursday, December 30, 2010
Best Vintage Stereo Reciever
Another year has ended and a new one begins. Hopefully the new one is better than its predecessor and comes packed with opportunities for all ...
This time I have not touched anything in the lottery of Christmas ... but it was logical given that he had not played. Completely lost faith in fate long ago. Wasting a euro in early does not hurt, but 20 euros and is too big and is not a good time to waste ...
Still, despite that they have become "taitantos" years that I have, I still find myself making wishes as every year, something unconscious that our brain does with the change of digit. I say I will be like a kind of electronic timing " we do with other minds and makes us feel united to each other with such enthusiasm, almost childlike, of believing that in future we will reach our expectations, desires, dreams ...
And to fulfill all our dreams then we harmonize our voices, raise our glasses and toast to the rhythm of each
wish us Happy New Year!
Monday, December 20, 2010
Rotel Chicken Velveeta Pasta Recipes
 Collisions between the cosmos and other universes may have left all the "bruises" on a map of ancient cosmic radiation.
Collisions between the cosmos and other universes may have left all the "bruises" on a map of ancient cosmic radiation. Our universe is believed to have spread rapidly in a process called inflation in the first moments after the Big Bang. Some physicists suspect inflation is occurring, the implementation in some regions while other stops as part of the universe we live in this picture, called eternal inflation, new universes are constantly popping into existence like bubbles in a vast, vast sea of \u200b\u200bspace-time.
Many of these universes should be taken to each other as soon as they are. But universes born together could crash if they are expanding faster than the space between them.
If our universe was beaten by another bubble universe, the impact statement would be colossal explosions of energy. If this happened before inflation ended in our review of the universe, could leave a mark that still might be detectable. Now Stephen Feeney, of University College London and colleagues say they may have discovered traces of its kind in the cosmic microwave background (CMB), the all-sky glow that comes from photons emitted when the universe was less than 400,000 years age.
Hot and Cold
A collision could alter the duration of inflation continued in the area of \u200b\u200bimpact. If the expansion continues for longer than it should, the density of matter in the impact zone would be lower than the surrounding regions. These show the CMB cold spot. By contrast, a shorter period of inflation could create a warm place in the CMB.
The team calculated the probable temperature profiles for this purpose and have searched the CMB data from NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe.
The search turned up four circular patches, each covering an area of \u200b\u200bsky equivalent to at least eight full moons (arxiv.org/abs/1012.1995 and arxiv.org/abs/1012.3667). One is a cold place that had been cited as evidence of another universe that interact with ours.
"There is no obvious explanation of the features dull," says team member Matthew Johnson of the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Waterloo, Canada.
Calling Cards
If collisions with other universes, in fact, creating these patches, which should have left other calling cards in the CMB, as characteristics that distinguish them in orientation, or polarization of the CMB photons. The satellite of ESA Planck, which was released in 2009, should be able to detect these signs. His first full-sky map is expected in 2012.
Even if only one of these points proves to be a clash of bubbles, which would be "a discovery of the first magnitude," says Thomas Levi, University of British Columbia in Vancouver, Canada. The findings reinforce the theories - such as string theory - which require a large number of universes with different properties.
"It is encouraging that there are some of the candidates," says Alexander Vilenkin of Tufts University in Medford, Massachusetts. But he adds that even if there bubble universes, could not be at a pace that guarantees would have clashed with our universe.
Church Help Request Letter
 If you want to see single atoms, it helps to have a powerful microscope. But in difficult situations as an atom at the edge of a sheet of carbon atoms, a high energy beam can disrupt the bonds that hold atoms of this type, making it difficult to study. Now for the first time, a low energy beam was used to having these bonds.
If you want to see single atoms, it helps to have a powerful microscope. But in difficult situations as an atom at the edge of a sheet of carbon atoms, a high energy beam can disrupt the bonds that hold atoms of this type, making it difficult to study. Now for the first time, a low energy beam was used to having these bonds. In the past, the beams of high energy electrons have been used to investigate the individual atoms. For example, as an electron beam is used to identify individual atoms-called "rare earth" elements were trapped inside buckyballs, round cage made of carbon atoms. By observing the energy spectra of electrons recovered, researchers can infer the size of the inside of the atom, and thus identify it.
probe atoms in other situations, however, may require more sensitive methods. Masanori Koshino, Kazu Suenaga and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology in Tsukuba, Japan, wanted to make measurements on carbon atoms cling to the edge of a sample of graphene - a sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal grid. In particular, became interested in the number of bonds holding the atoms of the edge in place, as this can affect the electrical and chemical properties of the graphene sheet.
In principle, the energy spectra of electrons scattered by an atom edge can be used to count the bonds. The problem is that a high electron beam energy can also reorder the edge atoms, changing the property itself to be measured.
Suenaga Koshino and took advantage of a new electron microscope that was able to accurately resolve the spectra of scattered electrons, even if they were of relatively low energy. Using electron beam with about 40 percent less energy than previous studies, the couple was able to resolve the spectra of electrons scattered by different atoms of graphene edge before the interruption occurred bond.
Friday, December 17, 2010
Cup Of Tea For Fasting
 In November 1895, the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered a "mysterious ray" that had the power to produce an image after passing through flesh, clothing, wood or metal and he baptized with the unknown "X". Since then the X-ray applications have multiplied. In addition to growing interest for medical diagnosis, this technology is used to control security at airports study the quality of cured ham or find the "missing matter in the universe." And even some have found a way to use X-rays for artistic purposes.
In November 1895, the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered a "mysterious ray" that had the power to produce an image after passing through flesh, clothing, wood or metal and he baptized with the unknown "X". Since then the X-ray applications have multiplied. In addition to growing interest for medical diagnosis, this technology is used to control security at airports study the quality of cured ham or find the "missing matter in the universe." And even some have found a way to use X-rays for artistic purposes. Naked clothing. airport in Manchester, England, has launched an X-ray scanners for passenger screening that can detect weapons, drugs or explosives at a glance. The aim is to improve security systems at airports. The device is not without controversy, as its use could be considered a violation of the right to privacy.
Genetics in action. Using X-ray crystallography, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania (USA) obtained a few months ago the first picture of the genetic processes that occur within each body cell.
X-ray telescopes Using two X-ray telescopes, the Chandra Observatory (NASA) and XMM-Newton (ESA), a team of astronomers has managed to find a huge intergalactic gas reserves located about 400 million light years from Earth, in what could be the "missing matter" of the universe that scientists have been looking for.
De pata negra. Computed tomography (CT) scanner normally called, is a medical diagnostic procedure that uses X-ray technology assisted by a computer to create multiple cross-sectional images of the body, by way of "slices", which together provide a complete picture 3D. Besides its medical importance, this technology is also used to visualize the process of salting a piece of ham, and to analyze the proportion of meat and fat.
Caring for the environment. X-ray spectroscopy have been used is what engineers and chemists at the University of Delaware, United States to develop a technique that measures in just a few milliseconds contamination in soil and water.
Wear your helmet. The Royal Air Force has developed a helmet that incorporates sophisticated X-rays and allows pilots to see through the walls of the aircraft. The device also incorporates anti-noise device and assists the pilot in navigation.
Fossils in amber. The European synchrotron facilities in Grenoble (France), paleontologists are using X-rays emitted by a particle accelerator to study pieces of amber English deposits from insects and spiders trapped inside for more than 100 million years. The technique allows them to view the content analysis of their digestive tracts and what to eat before getting caught, to study how their brains and see if flying without damaging the fossil.
Archimedes recovered. In 2006, researchers at Stanford University used a technique called X-ray fluorescence (XRF for its acronym in English) to expose a series of texts by the Greek mathematician and physicist Archimedes, one of the best minds of antiquity, that had been hidden under a series of images and texts for centuries.

tape "X". In 2008, the Laboratory of Acoustics and Low Temperature Physics Department, University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), Juan Valentín Escobar and his colleagues discovered that when a roll of adhesive tape that we handle daily off-load is the amount of X-rays are produced in 10 seconds is enough to get the x-ray of a human finger. The finding could lead to a more economical method to produce X-rays
Installation Sprinkler
 Until this year, all objects created by man by man have been moved in accordance with the laws of classical mechanics. But last March, physicists Andrew Cleland and John Martinis, University of California at Santa Barbara (USA), designed a device that "dances" and moves in a way that can only be described by quantum mechanics - the set of rules that governs the behavior of molecules, atoms and subatomic particles -. In recognition of the conceptual terrain in which their experiment is a pioneering, ingenuity behind it and its various applications potential, Science magazine has called this discovery the most significant scientific breakthrough of 2010.
Until this year, all objects created by man by man have been moved in accordance with the laws of classical mechanics. But last March, physicists Andrew Cleland and John Martinis, University of California at Santa Barbara (USA), designed a device that "dances" and moves in a way that can only be described by quantum mechanics - the set of rules that governs the behavior of molecules, atoms and subatomic particles -. In recognition of the conceptual terrain in which their experiment is a pioneering, ingenuity behind it and its various applications potential, Science magazine has called this discovery the most significant scientific breakthrough of 2010. addition, the publication has chosen another 9 scientific advances to be part of his "top ten" year. In the second set featuring developments in synthetic biology by Craig Venter and his team to create the first artificial bacterium genome. The list also includes other genetic landmarks, such as sequencing the Neanderthal genome from bones of three individuals who lived in Croatia between 38,000 and 44,000 years ago, advances in sequencing technologies that allows to launch initiatives such as the "Project of 1000 genomes ", the exons of a genome to study the so-called" rare diseases "and the reprogrammed cells using synthetic RNA.
Two new methods to prevent infection by the AIDS virus, advancements in the folding simulation protein, quantum simulators and the "return of the rats" to the laboratory for testing, complete the ranking.
A decade of science
addition, to celebrate the end of the decade, reporters and Science's editors have selected ten breakthroughs for science in the first decade of the millennium. It is nicknamed the "Genome Dark" (the non-coding genome, over 98%), the new "recipe" of the composition of the Cosmos, the study of ancient biomolecules (DNA, collagen ...) of tens of thousands of years old, finding water on Mars, the ability to reprogram and transform them into pluripotent cells, the microbiome, exoplanets, metamaterials and the first attempts to construct invisibility cloaks, advances in the study of inflammation and research climate change.
Free Std Testing Las Vegas

was released the names of people awarded this year's Gruber Cosmology Prize, which this time fell on a shared basis among astronomers Wendy Freedman (Canada), Robert Kennicutt (USA) Jeremy Mould (United Kingdom) for his work to help establish age of the universe. In particular, as announced by the president of the foundation, Patricia Gruber, the award was assigned to the three astronomers have made a definitive measurement of the rate of expansion of the universe, which is known as the Hubble constant.
I Need To Redo My Boat
few years ago astronomers thought that after the big bang of the Big Bang, the universe must be slowing. However, the study of distant supernovae revealed that the universe is expanding at an increasing rate. To explain this mysterious acceleration introduced the concept of dark energy.
Astrophysicists have worked with this scenario during the last decade, but this could be about to change. Smoller and Temple have just developed a model based on Einstein's equations to explain the anomalous acceleration of the universe without resorting to dark energy or cosmological constant (initially introduced by Einstein in his field equations of general relativity). Under the new theory, the universe would spread in waves, which would explain the acceleration of the galaxies.
Wednesday, December 15, 2010
Bronchial Antibiotics
 ven. The first is that the act of observation defines the world: there is no deep reality we live in a fantasy world where nothing exist until it is measured. The second is that in the subatomic world the notion of causality disappears, leaving only the probability of something happening. However, both will allow us to revolutionize the world of information. "There are plenty of free space in there." Thus began a conference on great physicist Richard Feynman. It was a warning about the huge amount of open space in the microscopic world inside the area. The current physical wonders why not exploit it and use it, for example, to transport, store and process information. That is precisely the goal of quantum information theory. Who could imagine the Library of U.S. Congress locked in the head of a pin? And not only that, but will allow us to encode this information so inviolable, quantum cryptography and build supercomputers capable of performing in a fraction of a second the same operations as a conventional computer would take several
ven. The first is that the act of observation defines the world: there is no deep reality we live in a fantasy world where nothing exist until it is measured. The second is that in the subatomic world the notion of causality disappears, leaving only the probability of something happening. However, both will allow us to revolutionize the world of information. "There are plenty of free space in there." Thus began a conference on great physicist Richard Feynman. It was a warning about the huge amount of open space in the microscopic world inside the area. The current physical wonders why not exploit it and use it, for example, to transport, store and process information. That is precisely the goal of quantum information theory. Who could imagine the Library of U.S. Congress locked in the head of a pin? And not only that, but will allow us to encode this information so inviolable, quantum cryptography and build supercomputers capable of performing in a fraction of a second the same operations as a conventional computer would take several million years to complete.
 ina steam. Nanoscience is, that is, the science of the very small. "Nano" is a prefix that is added to a magnitude to obtain a value of one billion times smaller. So, speaking of nanosystems involves objects smaller than bacteria. Physicists around the world working on projects whose ultimate goal is to control atomic-scale design new artificial materials. Devices have already been achieved as diverse as magnetic tunnel junctions, boxes and pumping systems quantum transistors that can control the flow of electrons one to one ... Here are the steps leading up to the nanorobots that flood the modern science fiction. The "nano" is fashionable.
ina steam. Nanoscience is, that is, the science of the very small. "Nano" is a prefix that is added to a magnitude to obtain a value of one billion times smaller. So, speaking of nanosystems involves objects smaller than bacteria. Physicists around the world working on projects whose ultimate goal is to control atomic-scale design new artificial materials. Devices have already been achieved as diverse as magnetic tunnel junctions, boxes and pumping systems quantum transistors that can control the flow of electrons one to one ... Here are the steps leading up to the nanorobots that flood the modern science fiction. The "nano" is fashionable.  s of experts met in ten years we will see in the market a new type of circuits in our computers, televisions and DVD players, electronics made with light. In 25 years, optical computers arrive, they will be much faster than today. And is that as we miniaturize more and more pieces of metal that are used to connect components on a chip will cause, among other problems, a loss of speed. The use of optical connections is an alternative, why not have these problems, but you have to find materials capable of controlling and guiding the propagation of light on a microscopic scale. However, to achieve an electronic exclusively with photons may be away or even ever get. For this reason, research in optoelectronics, ie, the design of circuits that use both electrons and photons. It tends to the bridge linking electronics to photonics and optical communications.
s of experts met in ten years we will see in the market a new type of circuits in our computers, televisions and DVD players, electronics made with light. In 25 years, optical computers arrive, they will be much faster than today. And is that as we miniaturize more and more pieces of metal that are used to connect components on a chip will cause, among other problems, a loss of speed. The use of optical connections is an alternative, why not have these problems, but you have to find materials capable of controlling and guiding the propagation of light on a microscopic scale. However, to achieve an electronic exclusively with photons may be away or even ever get. For this reason, research in optoelectronics, ie, the design of circuits that use both electrons and photons. It tends to the bridge linking electronics to photonics and optical communications.  quantum. Superconductors can conduct electrical current without losses and therefore can carry current densities over 2,000 times what a copper cable. Used in a multitude of devices from magnetic resonance equipment for hospitals, the magnetic fields produced by superconducting coils-up in detecting magnetic fields smaller than one billionth that of Earth. The drawback is that a material becomes superconducting by cooling much. The so-called high-temperature superconductors are materials that acquire this property when it comes down to -138 º C. What is not so clear is why they are superconductors. The classical theory, called BCS and enunciated in 1957, it fails. Today, superconductivity is a field of intense research. Discover a superconductor at room temperature is one of the new challenges.
quantum. Superconductors can conduct electrical current without losses and therefore can carry current densities over 2,000 times what a copper cable. Used in a multitude of devices from magnetic resonance equipment for hospitals, the magnetic fields produced by superconducting coils-up in detecting magnetic fields smaller than one billionth that of Earth. The drawback is that a material becomes superconducting by cooling much. The so-called high-temperature superconductors are materials that acquire this property when it comes down to -138 º C. What is not so clear is why they are superconductors. The classical theory, called BCS and enunciated in 1957, it fails. Today, superconductivity is a field of intense research. Discover a superconductor at room temperature is one of the new challenges. Treatment Maculopapular Rash
 art lasers have the power to create matter by capturing ghostly particles, according to quantum mechanics, permeate the apparently empty space.
art lasers have the power to create matter by capturing ghostly particles, according to quantum mechanics, permeate the apparently empty space. lasers which are concentrated around 1026 watts per square centimeter, this reaction out of effective control must convert the laser light in millions of electron-positron pairs, the team calculates.
But Pisin Chen of National Taiwan University in Taipei, says the cost of high-powered laser can make this method more expensive than the alternative. The standard way to create large numbers of positrons today is to shoot a beam of high energy electrons in a metal piece produce electron-positron pairs.
Tuesday, December 14, 2010
Can Ismell My Moms Feet
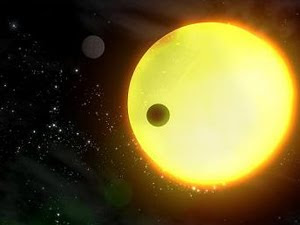 To weigh a star billions of miles balances and scales do not work. But astrophysicist David Kipping, Harvard University, has found it possible to calculate the exact weight of a star using a moon.
To weigh a star billions of miles balances and scales do not work. But astrophysicist David Kipping, Harvard University, has found it possible to calculate the exact weight of a star using a moon. If the star has a planet, and this in turn has a satellite, and they cross in front of the star, they may know a lot of the star, including how much it weighs. The process is not simple. First we must find out how light dims the star during the transit of the planet and the moon. This will get three measures: the orbital periods of two bodies: the relative size of their orbits against the star and the relative size of the planet and moon in relation to the star. "Using this information on Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion we can directly calculate the mass of the star," says Kipping, who insists that the method only works "if a family through."
Monday, December 13, 2010
Is There A Ds Game That's Like Poptropica?
"With these results we are opening the door through which scientists can find the missing links that allow us to understand how the universe formed and how it has evolved since then," said the director of Science and Robotic Exploration ESA , David Southwood.
According to NASA, this first full-sky image is a "special treasure, full of unpublished data for astronomers, as it reflects from the regions closest to the Milky Way to the limits of space and time. The disk of the Milky Way stretches across the center of the image. The first thing you notice is the filament of dust and gas extending above and below the galaxy, just where new stars are forming. More intriguing is the mottled background image, which presents the "cosmic microwave background '(CRMB, for its acronym in English), the oldest light in the Cosmos, with debris from the explosion that occurred about 13,700 million years and gave birth to the Universe.
Cosmic microwave fondoEl pattern is the fingerprint of what today forms the clusters and superclusters of galaxies, and can observe how the Cosmos was moments after its creation. The different colors represent tiny differences in temperature and density of matter in the universe. The CMBR is spread all over the map, but appears largely hidden behind the radiation from the Milky Way. Therefore, in the post-processing of data is deleted the contribution of the Milky Way to observe the cosmic background radiation in its entirety.
When this completed, Planck will be able to show the most accurate picture of the cosmic background radiation ever obtained. The big question now is whether the data may reveal the traces of primitive period known as "cosmic inflation." The hypothesis postulated that during this period, which took place just after the Big Bang, the universe expanded exponentially in a very short period of time. "This image is just a small taste of everything you can see Planck," he completed project scientist for the ESA Planck, Jan Tauber.
Sunday, December 12, 2010
Copy For A Vip Invitation
While a hydrogen atom consists of a proton and an electron, an atom of antihydrogen is formed by an antiproton and a positron. Antihydrogen was produced at low energies at CERN since 2002, but because when matter and antimatter are to "annihilate" each other, so far not been possible to confine these atoms, which prevented detailed study. Among the technical innovations that have enabled antimatter trap for the first time include a new 'cheat' magnetic confined to antihydrogen and prevents contact with the material.

Thursday, December 9, 2010
Kraft Creamy Italian Dressing Recipe
 In an experiment to collide lead nuclei at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, a team of British physicists has discovered that the early universe was not only extremely hot and dense, but also had a liquid consistency.
In an experiment to collide lead nuclei at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, a team of British physicists has discovered that the early universe was not only extremely hot and dense, but also had a liquid consistency. Who Does Sew In Louisville
 The Hubble Space r Fe my of NASA's Gamma-ray has revealed the existence of a vast and hitherto unknown structure in the center of the Milky Way. These two bubbles, 25,000 light years in diameter each, extending north and south of the galaxy.
The Hubble Space r Fe my of NASA's Gamma-ray has revealed the existence of a vast and hitherto unknown structure in the center of the Milky Way. These two bubbles, 25,000 light years in diameter each, extending north and south of the galaxy. Wednesday, December 8, 2010
Poptropica Do You Do Insp
 Almudena class , a teacher at a Secondary School, has been transformed into a chicken coop. "Jo, teacher, but we were not going to make a WebQuest? "complains one of the teenagers. She turns on the whiteboard and replied: "Caesar, sit down. I said that you open your laptop and internet conectéis: pop quiz. "
Almudena class , a teacher at a Secondary School, has been transformed into a chicken coop. "Jo, teacher, but we were not going to make a WebQuest? "complains one of the teenagers. She turns on the whiteboard and replied: "Caesar, sit down. I said that you open your laptop and internet conectéis: pop quiz. " The order seems incongruous. How will you evaluate the skills of their students with all the network before your eyes! It is feasible. This method has been tested in schools in Denmark and, if approved, there may be examined students connected to the Internet from 2011. It is seeking the necessary information to develop original work. To avoid copying, educators will check the pages visited.
For that matter, some people can chat, and Enrique Dans, professor of Information Systems at IE Business School in Madrid. "My students do their review on the laptop and send it to an email account. Before you let them use anything but chat. Now I do not, because a third person is a resource. "
Let's face learn how changed. Today we could not ensure the success of a television program as Time is money the late 80's and early 90's, in which a contestant was suffering from volume encyclopedia to find an enigmatic figure. "That look for it in Google! "I would say any adolescent. A digital divide separating young people of the generations that precede them, and in the classroom this gap is especially pronounced. Many teachers are digital immigrants in front of students, native to the cyberworld. Teachers have seen how sophisticated gadgets invade their centers, and provides a profound transformation in the way of generating and transmitting knowledge. Indeed, the explosion of Information Technology and Communication (ICT) in education is yet to come.
A Juan Manuel Núñez, director of corporate ICT SM Group in Madrid, his eyes shine when he imagines what still remains to be invented. "I do not believe in a futuristic room, but a new teaching supported powerful technologies. There will be more convergence between formal and non formal education, which takes place outside school, "will multiply the sources of knowledge, the teacher will be learning transmitter controller, there will be new devices from which you browse, read and write. And the student will not be the same. "
Finding The Impact Factor Of A Medical Journal
The researchers, led by Christian Marinoni and Adelina Buzzi, have overcome this problem by applying geometric proof pairs of distant galaxies in orbit. After calibrating the method using pairs of nearby galaxies, the authors found that the apparent geometry of distant pairs requires that the universe is flat. In addition, when data were combined with observations of clusters of galaxies to large scale, the data identify Einstein's cosmological constant, equivalent to a vacuum energy proposal, as the likely explanation for dark energy.
Saturday, December 4, 2010
Used Wooden Playsets Sale Ky
Nokia Morph is a concept that the Finnish company has developed in conjunction with the University of Cambridge, and the novelty is the use of nanotechnology for the construction of this device as the rumors point will be presented in 2015. Nokia Morph will be a cell flexible with the ability to bend and stretch, so we could both see videos considerable size and save it in your pocket.
Cell Nokia Morph is a semi-transparent, and has the ability to cleanse himself, among other characteristics that in itself would seem unnecessary, but will give the feeling Morph device out of a movie ; futuristic. An example of these utilities is shown that the cell can be folded into a wristwatch, this is taken together with a picture of a fund with dots, and the style chameleon, the cell , transforms and adopts the skin, looking like a bracelet. Another use would be interesting to analyze the air around food or other items to make sure they are in good condition. The Nokia Morph is a very ambitious project. Completion is scheduled for five years, although it may take a little longer. Even if so, this device seems to have the potential for a new revolution in mobile technology.
Substitute For Nesquick
Our present need for internet connectivity is so profound that secondary devices like the Nextep Computer are bound to happen. Developed to be worn as a bracelet, this computer concept is constructed out of a flexible OLED touchscreen. Earmarked for the year 2020, features like a holographic projector (for screen), pull-out extra keyboard panels and social networking compatibility, make the concept plausible. Ten years from now is not too far away, so how many of you think we’d be buying such gadgets?
Designer: Hiromi Kiriki
Awesome!
But in 2020? that's too much time to wait
How To Get Rid Of A Staph Scar
Samsung one of the leading companies in the electronics market, recently introduced in the FDP of Japan, its first prototypes of flexible displays AMOLED, in which record that the future of high-resolution panels for mobile phones and go through this type of panel.
During the technology fair developed in Japan, Samsung showed several types flexible displays, which were distinguished by size and resolution. The most powerful panel has a diagonal of 5.3 inches, a density of 235 dots per inch (or whatever it is, 960 x 800 pixels) and a 1,000,000:1 contrast and brightness index the height of an excellent monitor.




